Habits for Healthy Gums
Keeping your gums healthy and strong is essential for protecting your smile. Most patients know that regular dental exams and cleanings are good for their teeth. But they’re also crucial for preventing many oral problems, like receding gums.
Gum recession can cause uncomfortable symptoms and health risks. Although brushing and flossing away dental plaque at home can benefit gum health, other risk factors can lead to gum recession. To stop receding gums from getting worse, diagnosing and treating the cause is crucial.
What Is Gum Recession?
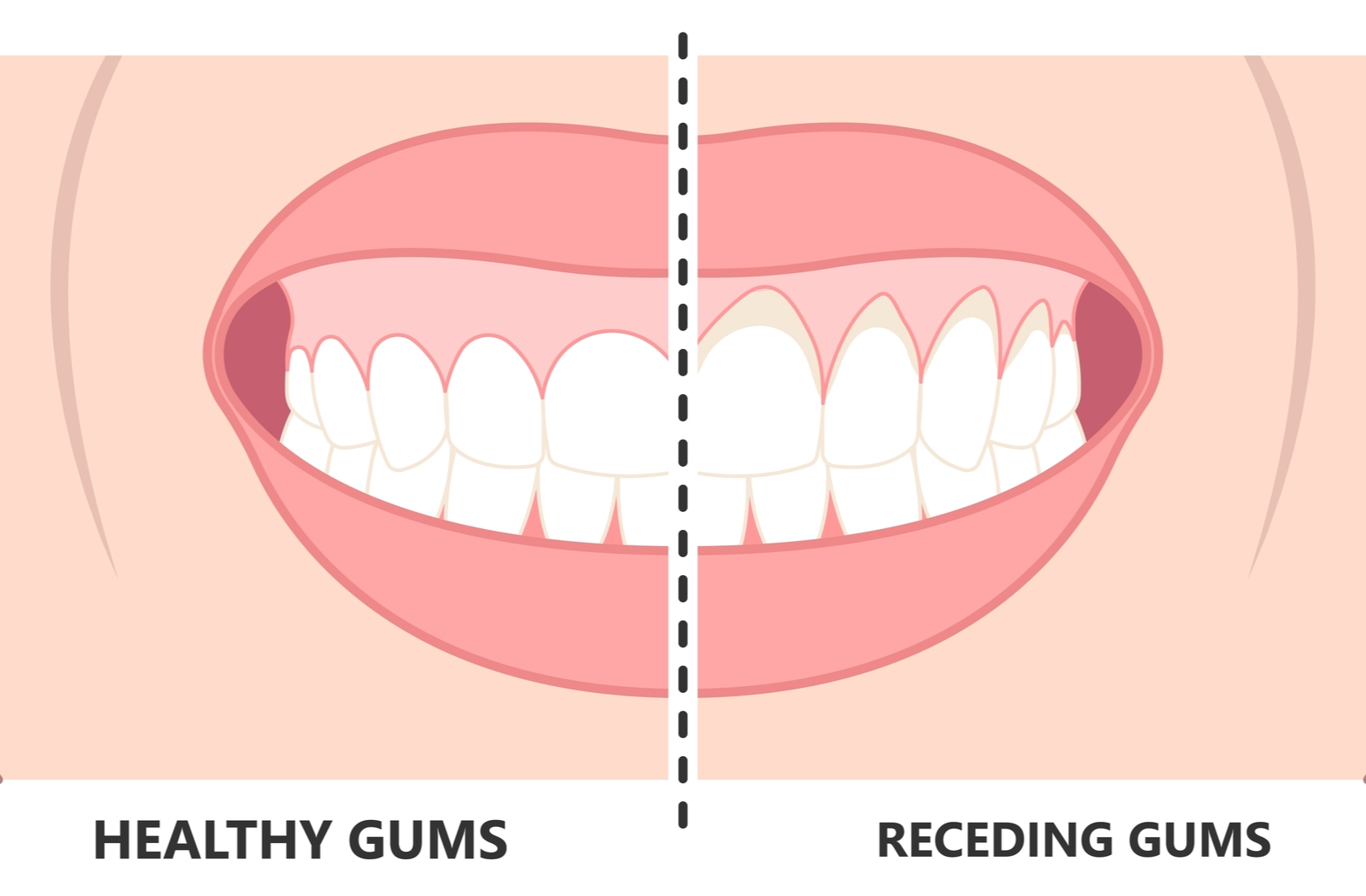
Healthy gums hug your teeth, fitting closely around the anatomical crown (top part of the tooth). Gingival recession (gum recession) is when your gums pull away from your teeth, loosening their hold on your teeth and exposing the roots.
Healthy gums support your teeth and oral health. They help secure your teeth and prevent bacteria from travelling to the more sensitive parts of the tooth. When the root is exposed, the tooth can appear elongated, and you may experience pain, swelling, sensitivity, and tooth discolouration. It also increases the risk of infection, often requiring root canal treatment.
Symptoms of receding gums typically include:
- Bleeding gums
- Exposed roots
- Loose teeth
- Pain at the gum lines
- Red or swollen gums
- Visibly shrinking gums
How to Stop Gum Recession
To stop receding gums from getting worse, you need to identify the cause. Your dentist can diagnose your dental health and recommend treatment options.
Some common causes of gum recession include:
- Aggressive brushing over time
- Bruxism (teeth & jaw clenching)
- Diabetes
- Gum disease
- Hormonal changes
- Plaque & tartar buildup
- Smoking
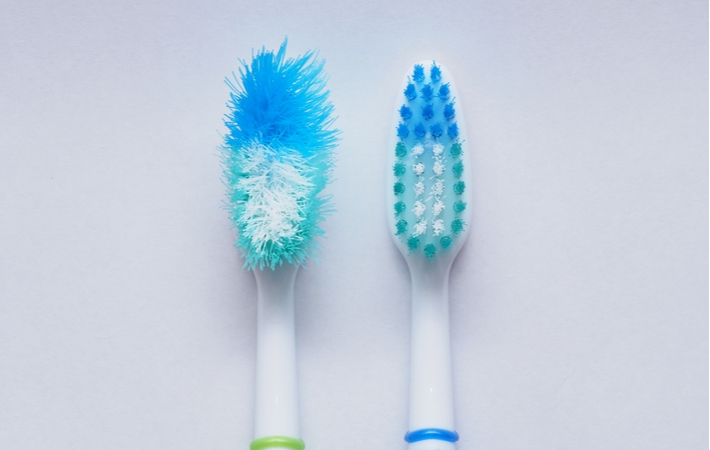

Aggressive Brushing
Brushing your teeth is an essential part of good oral hygiene. Regularly brushing (twice daily) can help prevent gum disease, tooth decay, and long-term oral health issues.
Unfortunately, incorrectly brushing can lead to oral problems. Brushing too hard, particularly along the gum line, can cause gum irritation. Over time, excessive pressure can cause gum recession.
To prevent aggressive brushing, try avoiding:
- Applying too much pressure while brushing
- Brushing with a broad, horizontal motion
- Using a hard-bristled toothbrush
If you’re having trouble decreasing the pressure, try switching to an electric toothbrush rather than a manual toothbrush. Some patients press harder with a manual brush.
Bruxism
Bruxism is the habit of teeth grinding and excessive jaw clenching. Over a prolonged period, the motion and intense pressure can cause gum recession. The grinding can also create deep pockets between the teeth and gums, causing:
- Bacteria buildup
- Gum inflammation
- Loose teeth
People often don’t realize they’re suffering from the condition, and many do so while sleeping. Bruxism while awake typically occurs when you’re tense and focused, such as working at a computer. Notably, more pressure is placed on the teeth while you’re asleep, contributing to grinding.
Often the first sign of night grinding is the sound. A partner, spouse, or parent is most likely to hear it. People who grind their teeth and clench their jaws may experience facial pain. However, the discomfort is typically minimal during the early days of the habit.
Try these tips to prevent bruxism and stop receding gums from getting worse:
- If you clench your jaw while awake, try to be more aware of the behaviour. Make note if it occurs more commonly during specific situations or tasks.
- Talk to your dentist about techniques for relaxing your jaw and keeping your teeth apart during the day.
- If you grind at night, try to practice relaxation techniques before bedtime, such as deep breathing, meditation, or listening to music.
- Include stress-reducing activities during the day, such as physical activity or relaxing hobbies.
Gum Disease
The most common cause of receding gums is gum disease (periodontal disease). When plaque hardens into tartar, a hard substance containing bacteria and acids, it destroys tooth enamel and surrounding tissue. Over time, the bacterial infection can erode gums, bones, and oral tissue.
Although gum disease typically progresses slowly, it can lead to multiple oral symptoms and increase the risk of heart disease, respiratory disorders, and stroke. However, gum disease is usually treatable and reversible, mainly when detected early.
Signs of gum disease typically include:
- Attachment loss (gum recession)
- Bad breath
- Bleeding gums
- Metallic taste
- Red or discoloured gums
- Shiny, puffy, or sore gums
- Tooth sensitivity
Your dentist can prescribe treatment options for gum disease. However, depending on the severity of the condition, a dentist may refer patients to a periodontist for treatment. Surgical treatment may sometimes be necessary to remove damaged teeth, gums, or tissue.
Treatment methods for gum disease include:
- Antibacterial toothpaste
- Antibacterial mouthwash
- Flap procedure
- Gingivectomy
- Root planing & scaling
- Topical or oral antibiotics
Preventing & Treating Gum Recession
Practicing healthy oral habits is the best way to prevent gum recession from worsening. Your at-home oral hygiene, including daily brushing, flossing, and nutrition, can significantly support your oral health. But when stubborn plaque buildup or oral health issues require more attention, your dentist can help.
Regular dental exams and cleanings are essential for keeping your gums healthy. Talk to your dentist if you’ve noticed changes in your gums or need tips about oral hygiene. Request an appointment with Ti Dental today!